Plastic exhaust pipes on a furnace indicate a high efficiency unit.
How does radiant heat flooring work and what are the two common types?
Radiant heat flooring is largely considered to be the most quality and luxurious method of home heating. Radiant heat floors rely on heat radiating from the floor into the home. This typically provides a more consistent and thorough heating than a forced air system where hot air is blown into a room.
There are two common methods for radiant heated floors:
1. Electric radiant heated floors:
This is most commonly used in retrofit applications and/or in smaller localized areas such as a primary bathroom or kitchen floor. Whole home electric installations are not typical.
2. Hot water radiant heated floors:
This method is most commonly used where the home's primary heating system is radiant heat floors. Hot water is produced in a boiler unit and then circulates through a series of pipes in or under the floor. Heat is transferred from the hot water into the space by way of radiant heating and then returns to the boiler to be reheated. Whole home radiant floor systems are generally designed to have multiple zones for optimal comfort and control.
What is the difference between a boiler and a furnace?
Is a sewer scope necessary on a home with a septic tank?
Yes. A sewer scope inspection is different and is generally a separate service than a septic tank inspection so you still want to have a sewer scope inspection conducted on a home with a septic tank.
A sewer scope inspects the condition of the sewer line from the home to the septic tank and a septic inspection strictly looks at the tank and leach field components. It is just as important to ensure that the sewer line is working properly for a home with a septic system as it is a municipal sewer system.
Can home water pressure be too high?
Yes. Domestic water pressure should be between 40-80 psi. Although strong water pressure is almost always desired by homeowners, pressure over 80 psi can lead to a host of issues and should be regulated.
Here are some issues with water pressure that is too high.
High water pressure can damage seals in fixtures and appliances causing premature failure and leakage.
“Water hammer” can occur when pressure is too high causing jolts in the water distribution system that lead to banging and knocking.
Excessively high water pressure can rupture supply hoses such as those to a refrigerator, dishwasher and washing machine. This is another reason why we always recommend braided stainless steel hoses that are more burst resistant.
What are the most common sewer line issues?
Without question, we advise every one of our clients to have a sewer scope performed as part of the home inspection. Why do we advise this? Simply put, sewer line issues are one of the most common home inspection issues with repairs being in the thousands of dollars.
Below is a list of the most common sewer line issues:
Blockages
Belly’s or low spots
Cracks or breaks
Separations or offsets
To learn more about sewer line issues, check out this blog post.
How long does a standard water heater typically last?
A standard tank water heater is typically expected to have a 12 year service life. Most water heaters come with a standard manufacturers warranty of 6 years, with options of up to 12 years. Generally tanks at or past 12 years are considered past expected service life.
Equipment age can be determined by following the date guide on the Building Intelligence Center website. Link: https://www.building-center.org/
Where does lead in water come from?
What are the maintenance requirements of a tankless water heater?
Tankless water heaters should be serviced annually by having the system flushed to remove scale buildup and deposits. Mineral buildup will reduce the efficiency of the heat exchanger and shorten the lifespan of the unit. Routine maintenance is particularly important in homes with hard water as scale buildup will occur more quickly. Cleaning of the air filter and water filter (if present) also need to be conducted on an annual basis to ensure proper operation.
How much does it cost to replace a water heater?
Replacement cost for a standard tank water heater can range from $800-$2800 depending on size, location, etc.
Replacement cost for a standard tankless water heater can range from $1200-$4800 depending on size, location, etc.
What is the difference between a sewage ejector pump and a sump pump?
Although sump pumps and sewage ejection systems, commonly referred to as “lift stations”, look similar at a glance, it’s important to know the difference between the two. Simply put, sump pumps handle and remove ground water, whereas sewage ejector pumps handle and pump domestic sewage produced by the use of plumbing fixtures in a home.
Sewage ejector pumps are necessary when the level of the sewer line is above the lowest plumbing fixture or drain line within a home. This is standard and necessary where a plumbing fixture has been installed in a basement with no previous plumbing, or commonly in new construction where an old home was demolished and replaced with a new home containing a basement. The level of the municipal sewer line cannot be lowered, so the home has to rely on a pump to “lift” the sewage to a point where it can naturally drain to the sewage by force of gravity. Sewage ejector pumps are typically identified by having a sealed lid with 2 pipes, whereas sump pumps often have only 1 pipe and may or may not have a sealed lid.
What is hard water?
“Hard water” is water that naturally has high mineral content due to the soil that it once percolated through. Municipal water can be hard in addition to private drinking wells due to the fact that municipal water treatment disinfects, but does not treat water mineral content. Hard water does not pose a health hazard, and can even offer some mild health benefits, but it can lead to dry skin, limescale and soap scum buildup. Hard water can also lead to premature failure of water using appliances as the scale buildup can reduce water flow. A water softening system can be installed to neutralize hard water if desired.
How to determine if you have hard water?
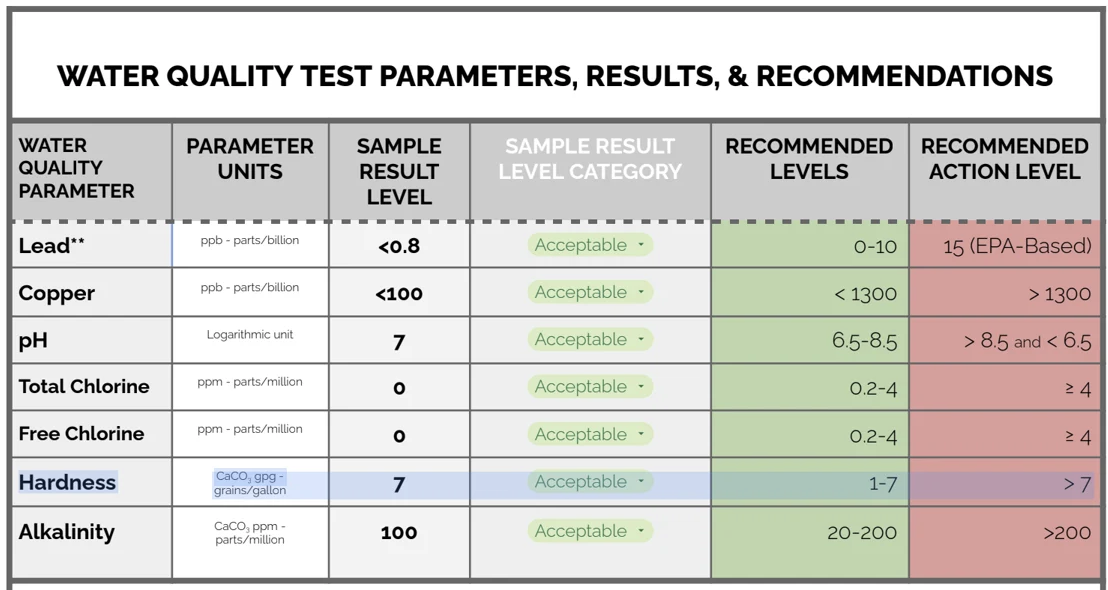
Water hardness is a measure of the concentration of minerals in the water, mainly magnesium and calcium. This can be measured and is one of the test parameters that is included in the ABP Water Quality Test. See the image below for sample results included in the ABP water quality test.
What is the problem with galvanized steel piping?
Galvanized steel water supply piping was a commonly used plumbing material from the 1880’s-1960’s. Initially used as an alternative to lead pipes, it was later learned that galvanized pipes heavily rust and corrode from the inside outward as the zinc coating wears off. In addition to failing and leakage, lead can also be introduced into the water supply from the galvanizing process. The expected service life of galvanized steel plumbing is around 60 years, so all galvanized steel plumbing is theoretically due for replacement by now.
What is Polybutylene plumbing and why is it a problem?
Polybutylene plumbing is a type of plastic resin water pipe that was a cheap and easy alternative to copper and was manufactured from 1975 to 1995. Polybutylene was banned in 1995 due to failure of pipes in the form of leaking and rupturing. Polybutylene is generally identified by its gray color with blue lettering usually stamped with “PB2110” and should be evaluated for replacement by a qualified plumbing contractor.
What Is Kitec Plumbing And Why Is It A Problem?
Kitec plumbing is a type of PEX water pipe that was manufactured from 1995 to 2007. Kitec was recalled in 2005 due to failure of pipes and fittings resulting in plumbing leaks. Kitec is generally identified by its bright orange or bright blue color and should be evaluated for replacement by a qualified plumbing contractor.
What Are the 2 Most Common Radon Testing Myths?
Myth 1 - Only homes with a basement can have high radon levels.
This is false. If the levels of radon in the soil are high enough, any home can have high radon levels whether or not the home is on a basement, crawlspace or slab foundation.
Myth 2 - The home has a mitigation system already installed so testing isn’t necessary.
This is also false. It’s true that a home with an active and properly functioning mitigation system is less likely to have high radon levels, but it’s important to confirm that the system is working properly. We perform many radon tests on homes with systems that come back with levels over 4pCi/L.
What Are The Different Types of Radon Mitigation Systems?
Radon is a colorless, odorless gas that can seep into buildings and pose a health risk to occupants. Radon mitigation systems are designed to reduce radon levels in buildings to safe levels. Here are some of the most common types of radon mitigation systems:
Active soil depressurization (ASD): This is the most common and effective type of radon mitigation system. It involves installing a vent pipe in the basement or crawl space of the building and connecting it to a fan that draws radon from the soil and exhausts it outside.
Passive soil depressurization: This type of system is similar to ASD, but it does not use a fan. Instead, it relies on natural air currents to draw radon from the soil and exhaust it outside.
Sub-slab depressurization: This system is used when the building has a concrete floor. It involves drilling a hole in the floor and inserting a pipe that is connected to a fan, which draws radon from the soil beneath the slab and exhausts it outside.
Sump pump suction: This system is used when the building has a sump pump. It involves installing a vent pipe in the sump pit and connecting it to a fan, which draws radon from the soil and exhausts it outside.
Block wall suction: This system is used when the building has a hollow block foundation. It involves drilling holes in the block and inserting pipes that are connected to a fan, which draws radon from the soil and exhausts it outside.
Crawlspace ventilation: This system is used in buildings with a crawlspace. It involves installing vents in the crawlspace walls and using a fan to draw in outside air, which dilutes the radon and exhausts it outside.
The type of radon mitigation system used depends on the specific conditions of the building and the level of radon present. It's important to work with a qualified and experienced professional to design and install a radon mitigation system that is appropriate for your building and effective in reducing radon levels to safe levels.
How Long Does A Deck Typically Last And How Often Often Should A Wood Deck Be Sealed?
The lifespan of a wood deck depends on several factors, including the type of wood used, the quality of the construction, the climate and weather conditions, and how well it is maintained. With proper care and maintenance, a wood deck can last anywhere from 10 to 50 years.
To ensure the longevity of your wood deck, it's important to keep it clean and well-maintained. Regular cleaning, staining, and sealing can help protect the wood from moisture, UV damage, and other types of wear and tear.
In general, a wood deck should be sealed or stained every one to three years, depending on the type of wood, the climate, and the level of use. A good rule of thumb is to perform a water test on your deck every year to determine whether it needs to be sealed. If water droplets bead up on the surface, the deck is still adequately sealed. If the water is absorbed into the wood, it's time to reseal.
Keep in mind that there are different types of sealers available, such as clear sealers, semi-transparent stains, and solid stains, each with different levels of protection and durability. It's important to choose a sealer that is appropriate for your climate and the level of use your deck receives. Additionally, regular maintenance such as cleaning and repairs can also help extend the lifespan of your deck.
How Often Should A Home With Wood Siding Be Re-Stained/Re-Sealed?
HOW OFTEN SHOULD A HOME WITH WOOD SIDING BE RE-STAINED/RE-SEALED?
We spoke with Kyler Williams, Owner of Dream Painting, to determine how often a home with wood siding should be re-stained or re-sealed. Please note that this email refers to staining/sealing of wood siding which is different than paint. Here is what Kyler had to say:
There are 4 types of wood siding stains and each type has a different service life. The general service life of each stain type is listed below and is based on when the stain begins to lose its original appearance.
Transparent/clear stain (2-3 years)
Semi Transparent stain (3-5 years)
Semi-solid stain (4-6 years)
Solid stain (5-7 years)
As you can see, the more solid the stain, the longer lasting it is.
Source - Kyler Williams, Owner of Dream Painting
What Is The Price Range To Replace A Garage Door And Motor?
We spoke with Louis Wilson of Ascent Garage Doors to get some answers about garage door and motor pricing. Here is what he had to say.
A garage door opener typically costs around $500 for a basic motor and $900 for a premium model.
The cost to replace a garage door depends on the door;
Hollow or vinyl backed single doors start at $1,000 and double doors at $1,700, but we do not recommend these types of doors, as they’re cheap and unreliable and will likely cost you more in the long run.
We recommend steel sandwich doors. They are much more durable and long lasting. Single doors start at $1,400 and doubles start at $2,300. Adding windows or wood grain colors or specialty insulation will increase the price about 30-50%.
More unique, boutique type doors can start at $3,000 single/$5,000 double and go up to $15,000 - $20,000 for double doors.
As you can tell, there are many options when replacing a garage door and garage door opener, so prices vary significantly.
Source - Louis Wilson of Ascent Garage Doors